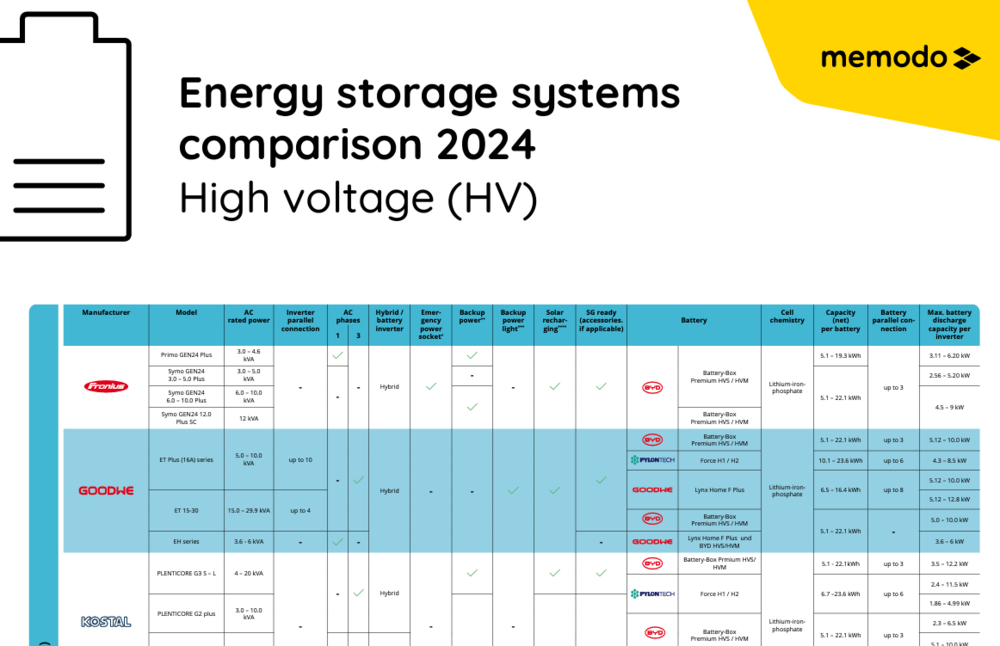
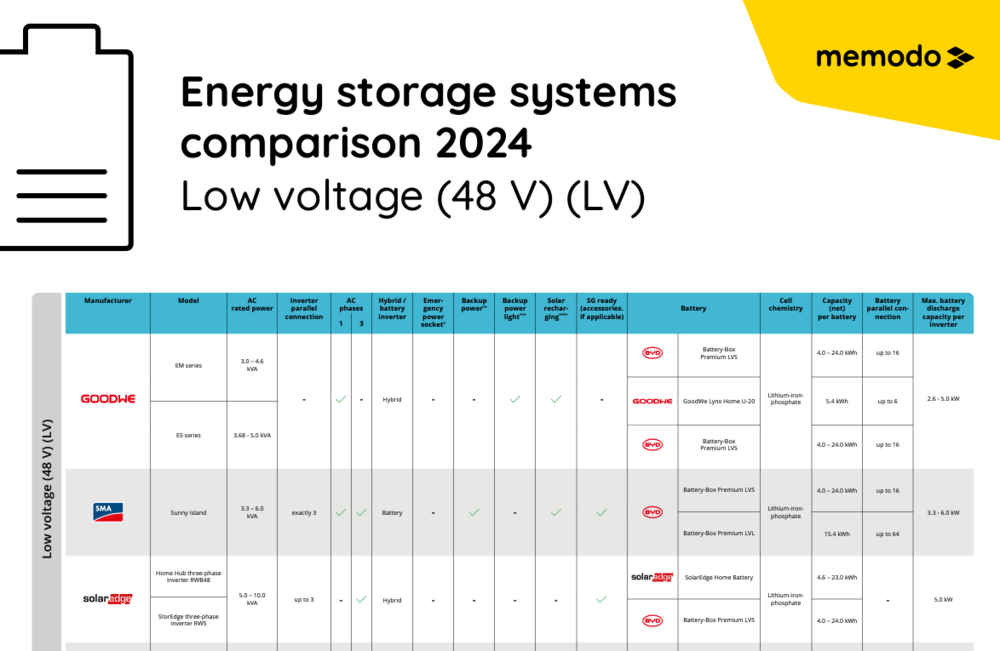
Energy Storage System Comparison
Our energy storage system comparison helps you to choose the right energy storage system for your photovoltaic project. An energy storage system increases the self-consumption using the solar energy generated by the solar system. In our energy storage comparison, we focus on lithium-ion batteries in the high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) range.
Our energy storage comparison puts Energizer storage system, Jinko Solar system, BYD storage systems, RCT storage systems and RCT inverters, Fronius inverters, KOSTAL inverters, LG Energy Solution storage systems, SMA inverters, SolarEdge battery storage systems and SolarEdge inverters, GoodWe storage, Sungrow battery storage systems and Sungrow inverters as well as BMZ systems in comparison. In addition to the price, the equipment, capacity and power also play an important role in choosing the right battery storage system.
Apart from this, each storage system has its own features and advantages, which we will examine in detail. Some systems, for example, are hybrid. Moreover, some storage systems are presented in a clear specific manner in an online portal and for some others the installation of the system is very easy.
If you are also looking for a suitable inverter, check out our energy storage system release list. Here you can find which energy storage model matches which inverter model.
Important parameters of the energy storage system comparison
Our energy storage system comparison is based on the following product features:
- AC phases (1-phase / 3-phase)
- Recommended solar-system size (kWp)
- DC coupling
- AC coupling
- Emergency power (for grid failure)
- Backup power (for grid failure)
- Solar recharging
- Cell chemistry
- Recommended battery capacity (gross in kWh)
- Expandability (battery retrofit)
- Charging and discharging capacity (kW)
The compatible battery packages and accessories
At Memodo you can find fully assembled battery packages which already include all the necessary accessories such as cables, energy meters (smart meters) or a battery connection set. Moreover, the suitable mounting system or substructure for photovoltaic systems on flat or pitched roofs is also available in our online shop.
Tip: Upgrade solar panels of your photovoltaic system with power optimizers to maximize the production of your solar system.
To make optimal use of self-consumption, we recommend connecting a charging station or a wallbox for an electric car or a hot water heat pump.
The right solar modules for your photovoltaic project
In addition to the storage system, the right solar panels are also important for a solar system. Depending on the application, we categorize them in high-performance solar panels, project solar panels, glass-glass solar panels and solar panels with integrated optimizers. When selecting a solar panel for your photovoltaic system, pay attention to the key features such as capacity, power, efficiency, temperature coefficient, open-circuit voltage, warranty periods, frame colour, backsheet colour and the module’s durability.
This is how we classify products in our energy storage system comparison:
Low voltage (48V) (LV)
Battery storage systems in the low-voltage range have an output voltage of 48 V. Low-voltage battery storage systems feature a fully developed and proven technology. It operates at the standard voltage level of system technology. Manufacturers offer a wide range of components in the 48 V range. The interconnection takes place in parallel and is scalable to high capacities.
High voltage (HV)
High-voltage technology is a relatively new concept in storage technologies. Each battery module has a voltage of 48 V. A high-voltage storage system contains several batteries with a total voltage of 200 - 500 V. This is created by connecting the individual battery modules in a series. This high output voltage results in a higher efficiency due to the reduction of conversion losses. If you install a high-voltage battery together with a hybrid inverter, you can build a very efficient storage system.
AC-Phases
Basically, there are 1-phase and 3-phase inverters. This applies not only for photovoltaic inverters, but also for battery inverters. 1-phase energy storage systems can supply up to 4.6 kW to the household grid. If the consumption is greater or the desired power is more than 13.8 kW, a 3-phase system is necessary. Otherwise, the single-phase storage systems are also sufficient.
Recommended system size (kWp)
If possible, the battery storage system should be adapted to the size of the photovoltaic system (kWp). Choosing the right storage system in terms of annual electricity consumption (kWh) and expected annual yield makes the system cost-effective.
DC Coupling
Another factor for the optimal comparison of an energy storage system is the coupling of the photovoltaic system with the energy source. With DC coupling (direct current), the production system and the battery storage unit share the same inverter - both components are thus unified. The advantage: the energy produced by the photovoltaic system, which flows via the battery to the consumers, only completes the direct current to alternating current conversion once.
DC systems are particularly suitable for new installations. Moreover, the maximum photovoltaic system size for direct charging of the battery is limited here. A significant advantage of DC systems is that you need fewer components, which also minimises the installation effort.
AC coupling
AC coupling (alternating current) is optimal when you retrofit a battery storage system. In contrast to the DC system, the photovoltaic system and the battery storage system each have their own inverter.
Emergency power
Energy storage systems with an emergency power connection supply power to devices in the event of a grid failure. The connection is usually made by manually activating the integrated emergency power connection. The available power is usually limited to 1-phase appliances in the house.
Backup power
Backup power provides power to the appliances in the event of a grid failure by using the in-house power stored in the battery storage system. The switchover takes place automatically after approx. 5 - 20 seconds, usually via a switchover device and involves additional installation work. The backup power grid is set up as a 1-phase or 3-phase system.
Solar recharging
In case of emergency power/back-up power operation, energy storage systems that have a solar recharging function are recharged on the DC side via the photovoltaic system. If, for example, there is a power failure on a sunny day, then thanks to the solar recharging functionality the battery can continue to be charged with solar power from the photovoltaic system. As usual this electricity can be used at night.
Cell chemistry
The cell chemistry of a battery inverter provides information about the safety, longevity and efficiency as well as the environmental sustainability of the device.
Capacity
The storage capacity, measured in kWh, describes the maximum amount of energy the battery can store. In the residential sector, storage capacities currently range between approx. 3 and 14 kWh. The usage capacity of a battery indicates the actual capacity or net capacity. The latter always depends on the respective depth of discharge or loading limit.
Expandability
The expandability of a storage system is an important parameter when it comes to flexible retrofitting. If you decide to buy an e-vehicle or other electricity appliances are installed, the annual energy consumption may change. In this case, it makes sense to subsequently expand the storage system. As a rule, you should retrofit the battery within one year, but there are also manufacturers who enable a longer time period.
Max. charging and discharging power
The charging and discharging capacity of a battery indicates how much power can be supplied or withdrawn. You choose the right storage system based on the user's requirements for the battery.