Data Protection in Photovoltaics: 10 Questions (and Answers)
Digitalisation in photovoltaics is making life easier than ever, enabling fully integrated PV systems through sector coupling. But sector coupling also means data transfer and that makes cybersecurity and data protection more crucial than ever. In this guide, we answer the 10 most important questions you and your customers should be asking about data protection in photovoltaics.
Data Protection and Solar installations: Why is it important?
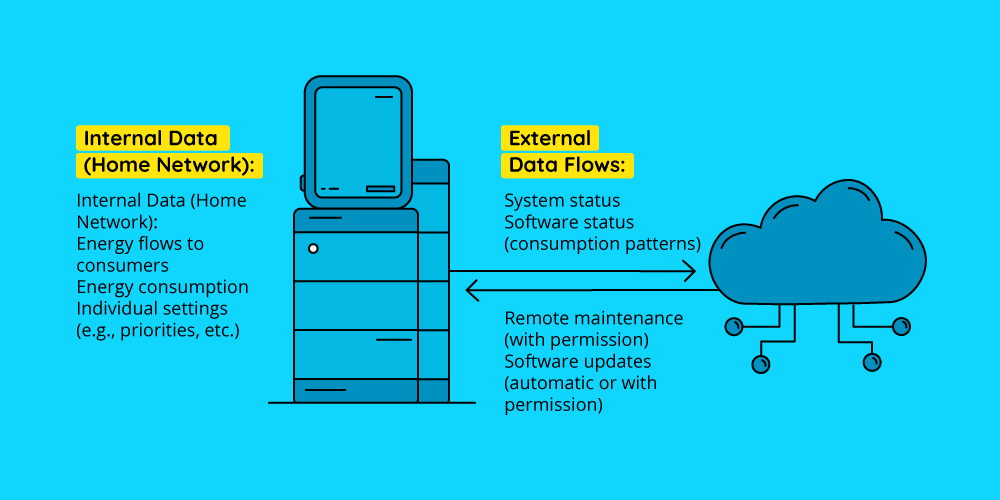
Installers nowadays monitor many PV systems remotely and system operators have constant access to all performance data through cloud-based services. Additionally, the energy management system (EMS) uses Wi-Fi to control energy flows within the household. For these systems to function effectively, devices must continuously collect and exchange data. It’s not only about the cybersecurity, which is protecting systems from digital attacks, but your customers must always have full control over the data they share. That's why data protection is just as critical to the safety concept of a PV system as overvoltage protection, fire safety, and cybersecurity itself.
General questions about data protection in PV
While the internet itself is no longer uncharted territory, data protection in photovoltaics certainly is. Let's start by addressing some fundamental questions:
1. Who collects data from your PV system?
Performance and system data are typically sent to:
- Inverter manufacturers
- Manufacturers of EV chargers (wallboxes) and battery storage systems
- Grid operators
- Metering service providers
- Your remote monitoring devices
Tip: Check the manufacturer's privacy policy to find detailed information on exactly which data is collected and where it's transmitted.
2. What kind of data does a PV system collect?
Every PV system collects the following data:
System allocation
System data, installed devices, and household details.
System status
Status notifications, maintenance intervals, and error messages.
Performance data
Power generation and consumption, system voltage, and feed-in power.
Smart, connected systems typically also collect:
Usage data
Detailed electricity consumption of individual appliances, including usage times and consumption profiles (e.g., for EMS).
Location data
This allows smart systems to record grid and weather information to optimise power consumption.
Tip: You can customise data collection and sharing preferences in the device settings. However, restricting data sharing may limit the availability of certain features.
3. Where is your PV system data stored?
Many types of data, such as usage information, are processed exclusively within the system itself. However, many manufacturers also use cloud-based solutions, this is especially common with modern energy management systems. Additionally, when you perform remote maintenance, system data is processed on your work devices. It is therefore very important to pay attention to cybersecurity in your company too.
Tip: Ensure that cloud servers are located in the EU, where strict data protection and consumer privacy standards apply. Most manufacturers already use servers based in EU countries to comply with these standards.
4. Which standards apply to data protection in photovoltaics?
The most important standard is ISO 27001, which defines the standards for data security in IT systems. Many well-known manufacturers such as Fronius, SMA, Solar Manager, SolarEdge and many others comply with this standard.
Tip: To check if a device is ISO 27001 compliant, search for ISO 27001 on the manufacturer's website or privacy policy using a full-text search (Ctrl-F or Apple-F).
5. What role does GDPR play in photovoltaics?
The EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) protects personal data. In photovoltaics, this particularly applies to data that could identify PV system operators, such as:
- Consumption profiles
- Location data
- Payment information
The GDPR requires a "double opt-in," meaning your customers must explicitly consent to the use of their data. This ensures that your customers remain in control of their data at all times.
Tip: Any breaches of the GDPR can be reported directly to your local data protection authority.
Data protection for inverters, solar energy storage systems and wallboxes
As mentioned above, most PV devices collect data in order to operate efficiently. Below is an overview of the data typically collected by each device. Note: For commercial PV systems, it's important to coordinate with the company's IT department to ensure proper compliance.
6. What data does an inverter collect?
Inverters primarily collect and process output-related data. This data is useful for system monitoring and fault analysis.
Tip:You can only access the system from the outside if the system operators allow it via the app.
7. Where is the data from the battery storage system stored?
Battery storage systems track charging and discharging cycles as well as the storage capacity. This data is stored either locally on the device or in the cloud. This information is essential for energy management systems to work efficiently.
Tip:Set up local data storage options if needed.
8.What data does a wallbox collect?
Modern wallboxes collect data such as charging times, charging duration and charging power. This allows households to keep track of the wallbox's performance at all times.
Tip: Review the wallbox data with your customers and explain what it means.
Data Protection and EMS: Connected networks
Data protection will be unavoidable in the future: As energy management systems (EMS) become increasingly widespread, interconnected PV systems will emerge as the new industry norm.
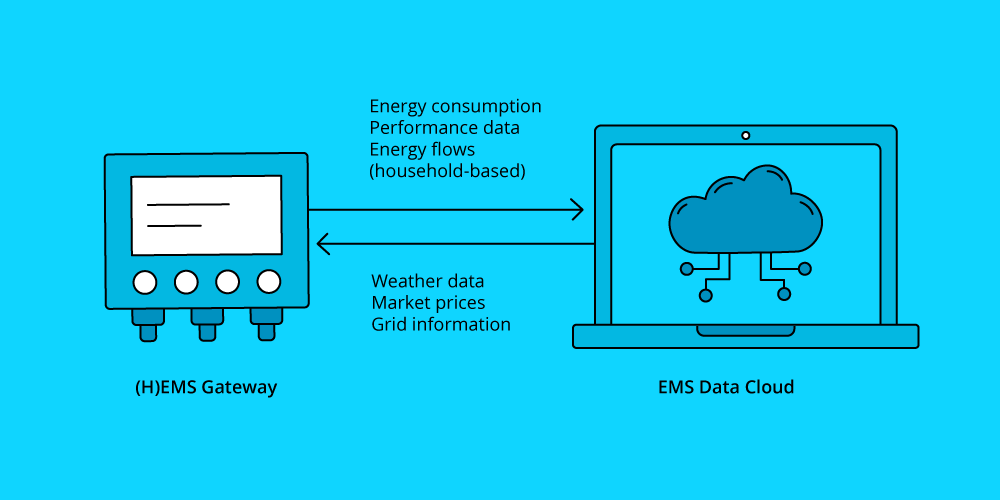
9. How does data protection work with an Energy Management System (EMS)?
Modern EMSs typically operate in a fully networked way: the systems process and transmit data - this is the only way they can optimally balance energy flows within a household. Make sure you consider the following points:
Encryption
Ensure that all data is transmitted in encrypted form. Ideally, opt for dual encryption – both at the sender end (the EMS) and at the receiver end (the data cloud).
Server location
A server located within the EU is subject to particularly high data protection standards.
Access only with opt-in
The manufacturer's software should only allow remote access to read or modify data with the explicit permission of the user.
Manufacturers such as SolarEdge ONE is highly aware of data protection requirements and are fully compliant with both GDPR regulations and ISO 27001 standards. Their respective privacy policies can be found here:
Tip: Set up the EMS app and access permissions together with your customers directly on their devices.
10. What data protection regulations apply to smart meters?
By 2030, most photovoltaic (PV) systems are expected to be equipped with a smart meter. These devices are essential for enabling grid-friendly energy management, particularly in response to rising decentralised generation and dynamic grid demands. In most EU member states, access to smart meter data is strictly regulated: Only the authorised metering operator can access the data transmitted by the smart meter.
Tip: Data protection rules for smart metering are strict across the EU.
Conclusion – How important is data protection in the PV sector?
Data protection in the PV sector is becoming increasingly important as the solar industry becomes more digital. As a PV professional, it’s now part of your role to advise customers on data protection and to consider it when planning system concepts. The high data protection standards across the EU provide a solid foundation and make compliance more manageable. If you have specific questions about data protection in PV systems, it's best to check the manufacturer's terms and conditions or contact your Memodo partner for expert support.